Last Updated on August 27, 2024 by Admin
When selecting a projector, one of the most crucial factors to consider is its resolution. In today’s world, where visual experiences are increasingly central to entertainment, education, and business, the resolution of a projector screen plays a crucial role.
Whether you’re setting up a home theater, preparing for a business presentation, or enjoying a gaming session, understanding projector screen resolutions can significantly impact your viewing experience.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the different types of projector screen resolutions (SVGA, XGA, SXGA, UXGA, WXGA, WXGA+, WUXGA, SD, HD, Full HD, 2K, 4K, and 8K), their importance, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
Page Contents
What is Projector Screen Resolution?
Projector screen resolution refers to the number of pixels that compose the image displayed on the screen. A pixel is the smallest unit of a digital image, and the more pixels a projector can display, the sharper and more detailed the image will be. Resolution is typically represented by the number of pixels horizontally by the number of pixels vertically, such as 1920 x 1080, which represents Full HD resolution.
Example:
For example, an HD video with a resolution of 1280 x 720 pixels has 1280 pixels horizontally and 720 pixels vertically. This means it contains a total of 921,600 pixels. The clarity and quality of the image depend on using the correct resolution for the screen size.
Why Resolution Matters in Projectors
Resolution is one of several important factors to consider when purchasing a projector, alongside brightness (measured in lumens), screen size, and contrast ratio. It’s important to match the projector’s resolution with the resolution of the content you plan to display.
For instance, if you have a projector with a resolution of 800 x 600 pixels (SVGA) and you play a video with a resolution of 1920 x 1080 pixels (Full HD), the projector will downscale the video to fit its native resolution. This can result in a loss of detail and clarity.
Resolution Vs Screen Size:
While screen size refers to the physical dimensions of the screen, resolution indicates the number of pixels that make up the image. Even if you have a large screen, a lower resolution will result in a pixelated image if the pixel count isn’t sufficient for the screen size. Therefore, choosing the right resolution for your screen size is critical to achieving a sharp and clear image.
Check out How to Measure the Screen Size.
Types of Resolutions:
Some of the important factors while buying a Projector are Projecting Resolution, Lumens, Screen Size, and Contrast Ratio. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the Types of Resolutions before choosing a Projector.
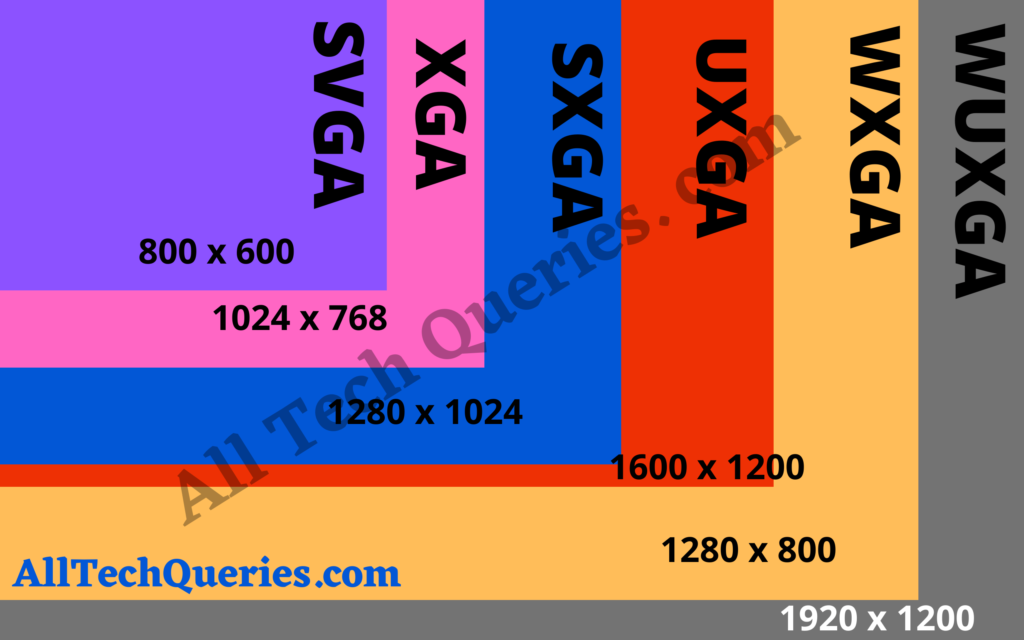
SVGA (800 x 600 pixels):
Description: SVGA, or Super Video Graphics Array, is one of the oldest projector resolutions, with an Aspect Ratio of 4:3.
Best For: Suitable for watching older movies, playing classic games, or viewing simple presentations. This was the standard resolution in the early days of projectors.
Limitation: Not suitable for high-definition video or detailed images due to its lower pixel count.
XGA (1024 x 768 pixels):
Description: XGA stands for Extended Graphics Array, an improvement over SVGA with the same 4:3 aspect ratio.
Best For: Ideal for basic presentations and standard-definition content, offering better clarity than SVGA.
Limitation: While an improvement over SVGA, XGA still lacks the detail required for full HD content.
SXGA (1280 x 1024 pixels):
Description: SXGA, or Super Extended Graphics Array, offers a higher resolution with an aspect ratio of 5:4.
SXGA has a Resolution of 1280 x 1024, with an Aspect Ratio of 5:4.
There are sub-categories in SXGA with minor changes in the Resolution.
Subcategories include:
SXGA-: 1280 x 960 pixels with a 4:3 aspect ratio.
SXGA+: 1400 x 1050 pixels with a 4:3 aspect ratio.
Best For: Suitable for more detailed presentations and content requiring higher resolution.
UXGA (1600 x 1200 pixels):
Description: UXGA, or Ultra Extended Graphics Array, offers a higher resolution with a 4:3 aspect ratio.
Best For: Ideal for professional environments where high detail is necessary.
WXGA (1280 x 800 pixels)
Description: WXGA stands for Wide XGA, offering a wider aspect ratio of 16:10.
Best For: Suitable for widescreen presentations and HD content.
Limitation: Not as detailed as Full HD, but sufficient for most standard-definition content.
WXGA+ (1440 x 900 pixels)
Description: WXGA+ offers an even higher resolution with a 16:10 aspect ratio.
Best For: Excellent for HD content with a more cinematic feel.
WUXGA (1920 x 1200 pixels)
Description: WUXGA, or Wide Ultra Extended Graphics Array, offers a resolution of 1920 x 1200 pixels with a 16:10 aspect ratio.
Best For: Ideal for professional presentations, CAD drawings, and high-definition video content.
More Resolutions:
In addition to the resolutions used in projectors, there are several other common resolutions found in various electronic devices like TVs and digital cameras. These include SD, HD, Full HD, 2K, 4K, and more.
These resolutions are often referred to by their shorthand names, such as 144p, 240p, 720p, 1080p, etc. The shorthand is typically derived from the lower end of the resolution scale.
For instance, a resolution of 720 x 480 pixels isn’t called 720p; instead, it’s referred to as 480p or SD, based on the lower pixel count. Similarly, a resolution of 1920 x 1080 pixels is commonly known as 1080p.
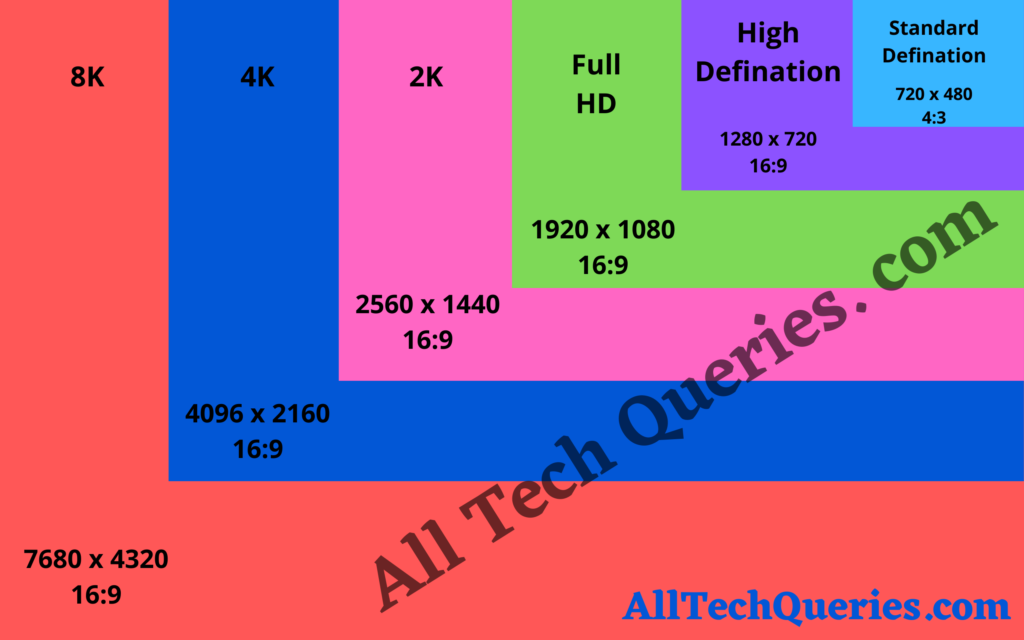
SD (720 x 480):
Description: SD, or Standard Definition, was widely used in the past. It features a resolution of 720 x 480 pixels and has an aspect ratio of 4:3.
HD (1280 x 720 pixels):
Description: HD stands for High Definition and offers a resolution of 1280 x 720 pixels, commonly referred to as 720p. This resolution is popular and typically comes with a 16:9 aspect ratio.
Full HD (1920 x 1080 pixels)
Description: Full HD offers a resolution of 1920 x 1080 pixels with a 16:9 aspect ratio.
Best For: Perfect for home theaters, gaming, and detailed presentations.
Limitation: While very clear, it’s not as sharp as 4K when viewed on very large screens.
2K (2560 x 1440 pixels)
Description: 2K resolution offers greater clarity than Full HD, with a 16:9 aspect ratio.
Best For: Suitable for high-end gaming and detailed professional work.
4K UHD (3840 x 2160 pixels)
Description: 4K Ultra High Definition provides four times the resolution of Full HD, with a 16:9 aspect ratio.
Best For: Best for home theaters, professional presentations, and any application requiring ultra-high definition.
Limitation: More expensive and requires more processing power, but the quality is unmatched.
8K (7680 x 4320 pixels)
Description: 8K resolution is the latest and highest resolution available, with a 16:9 aspect ratio.
Best For: Specialized applications, such as large venue displays or scientific purposes.
Limitation: Rare in consumer projectors, extremely expensive, and requires content specifically produced in 8K.
Understanding Resolution Acronyms and Their Importance
Here is a breakdown of common resolutions used in projectors and other electronic devices, like TVs and digital cameras:
- SD (480p): 720 x 480 pixels, aspect ratio 4:3
- HD (720p): 1280 x 720 pixels, aspect ratio 16:9
- Full HD (1080p): 1920 x 1080 pixels, aspect ratio 16:9
- 2K: 2560 x 1440 pixels, aspect ratio 16:9
- 4K: 4096 x 2160 pixels, aspect ratio 16:9
- 8K: 7680 x 4320 pixels, aspect ratio 16:9
Projector Resolution Chart:
The following chart will help you identify and understand the Screen Resolutions better.
| Resolution | Acronym | Pixels Horizontally | Pixels Vertically | Total Pixels | Aspect Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Super Video Graphics Array | SVGA | 800 | 600 | 480,000 | 4:3 |
| Extended Graphics Array | XGA | 1024 | 768 | 786,000 | 4:3 |
| Super Extended Graphics Array | SXGA | 1280 | 1024 | 1,470,000 | 5:4 |
| Super Extended Graphics Array – | SXGA – | 1280 | 960 | 1,228,800 | 4:3 |
| Super Extended Graphics Array + | SXGA+ | 1400 | 1050 | 1,470,000 | 4:3 |
| Ultra Extended Graphics Array | UXGA | 1600 | 1200 | 1,920,000 | 4:3 |
| Wide Extended Graphics Array | WXGA | 1280 | 800 | 1,024,000 | 16:10 |
| Wide Extended Graphics Array + | WXGA+ | 1440 | 900 | 1,296,000 | 16:10 |
| Wide Ultra Extended Graphics Array | WUXGA | 1920 | 1200 | 2,304,000 | 16:10 |
| Standard Definition | SD (480p) | 720 | 480 | 345,600 | 4:3 |
| High Definition | HD (720p) | 1280 | 720 | 921,600 | 16:9 |
| Full High Definition | Full HD (1080p) | 1920 | 1080 | 2,073,600 | 16:9 |
| 2K | 2K | 2560 | 1440 | 3,686,400 | 16:9 |
| 4K | 4K | 4096 | 2160 | 8,847,360 | 16:9 |
| 8K | 8K | 7680 | 4320 | 33,177,600 | 16:9 |
How Resolution Affects Image Quality
The impact of projector screen resolutions on image quality is significant. Higher resolutions mean more pixels, which translates to sharper, clearer images. This is particularly important when projecting on large screens, as lower resolutions may result in pixelated images that detract from the viewing experience.
- Pixel Density: Higher pixel density (more pixels per inch) results in smoother images with less visible pixelation.
- Screen Size and Viewing Distance: The larger the screen or the closer the viewing distance, the more noticeable the resolution. For instance, a Full HD resolution might look sharp on a smaller screen, but on a larger screen, the difference between Full HD and 4K becomes evident.
Choosing the Right Projector Screen Resolution for Your Needs
Selecting the right projector resolution depends on several factors:
- Usage: For basic presentations or educational purposes, a lower resolution like XGA or WXGA might suffice. However, for home theaters, gaming, or professional use, a higher resolution like Full HD or 4K is advisable.
- Budget: Higher resolutions generally come with a higher price tag. Balancing your need for clarity with your budget is essential.
- Screen Size: Larger screens benefit more from higher resolutions. A small projector screen might not show much difference between 1080p and 4K, but on a large screen, the difference can be dramatic.
Comparing Different Resolutions
To further understand how different projector screen resolutions compare, here’s a brief overview:
- SVGA vs. XGA: XGA offers more clarity and is better suited for presentations that include more detailed images or small text.
- WXGA vs. Full HD: WXGA is good for standard HD content, but Full HD provides a noticeable improvement in detail and is better for movies and games.
- Full HD vs. 4K: 4K offers four times the resolution of Full HD, resulting in much sharper images, especially on larger screens.
Future Trends in Projector Resolutions
As technology advances, we’re seeing a push towards even higher resolutions like 8K. While currently rare and expensive, 8K projectors represent the future of ultra-high-definition projection. As content becomes more available in these resolutions, it’s likely that we will see broader adoption.
Conclusion:
Understanding projector screen resolutions is crucial when selecting a projector for your specific needs. Whether you are purchasing a projector for a home theater, business presentations, or professional work, knowing the various types of resolutions, such as SVGA, XGA, SXGA, UXGA, WXGA, WUXGA, HD, Full HD, 2K, 4K, and 8K, will help you make an informed decision. Each resolution offers different levels of detail and clarity, impacting the overall viewing experience.
My Opinion
For most users, a Full HD (1080p) projector provides an excellent balance between price and performance, making it a popular choice for home theaters and general use. However, if you seek the highest level of detail and image quality, a 4K projector might be the best option. Understanding projector screen resolutions will ensure that you choose a projector that meets your needs and provides the best possible viewing experience.