Last Updated on August 14, 2024 by Admin
Typically, projectors are positioned in front of the screen, but did you know they can also be placed behind it? This setup is known as rear projection.
When it comes to setting up a projection system, whether for a home theater, office presentation, or large event, one crucial decision is choosing between front projection Vs rear projection.
Each method has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to understand the difference between front and rear projection before making your choice.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into difference between rear projection vs front projection, exploring how they work, their pros and cons, and which one might be the best fit for your needs.
Page Contents
What is Front Projection?
Front projection is the most common and traditional method of projection. In this setup, the projector is placed in front of the screen, and the image is projected directly onto it. The audience sits behind the projector, facing the screen.
In Simple words, the Projector is placed in front of the Projector Screen or Wall. The audience sits on the same side.
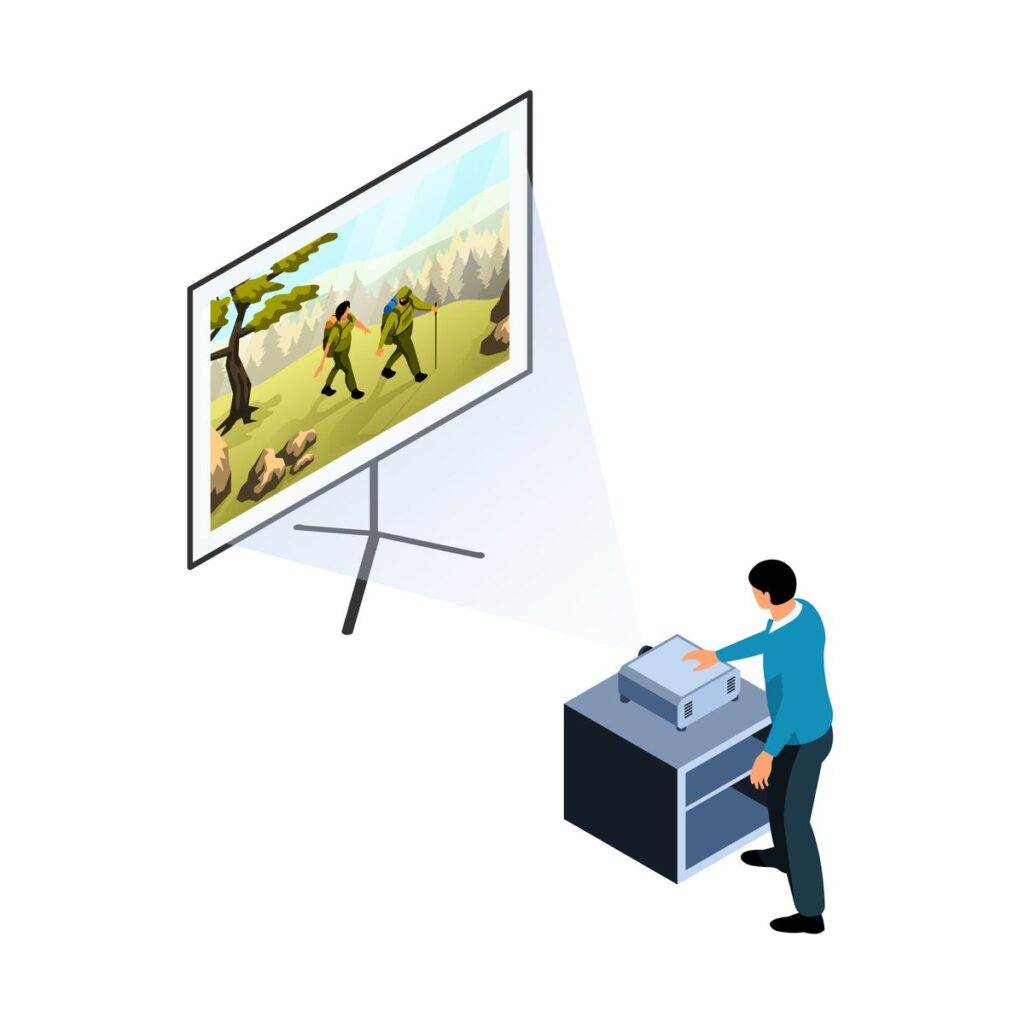

Key Features of Front Projection:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Front projection systems are generally more affordable and widely available.
- Simple Setup: Easy to install, with fewer specialized requirements.
- Versatility: Suitable for various environments, including home theaters, classrooms, and conference rooms.
Advantages of Front Projection:
- Affordability: Front projection is typically less expensive, both in terms of the projector and the screen.
- Ease of Use: Most projectors are designed for front projection, making them user-friendly and easy to set up.
- Flexibility: Can be used in a variety of settings, from small home theaters to large conference rooms.
Disadvantages of Front Projection:
- Shadows and Obstructions: People or objects passing in front of the projector can cast shadows on the screen.
- Ambient Light Sensitivity: Front projection systems are more affected by ambient light, which can wash out the image if the room isn’t properly darkened.
- Visible Equipment: The projector and cables are typically visible, which may not be aesthetically pleasing in some setups.
What is Rear Projection?
Rear projection offers a different approach. In this setup, the projector is placed behind the screen, and the image is projected through the screen to the audience. This method is often used in professional environments, such as trade shows, digital signage, and large venues.
In simple words, the Projector is placed behind the Projector Screen. The audience sits on the other side.

Key Features of Rear Projection:
- No Shadows: Since the projector is behind the screen, there’s no risk of shadows being cast on the image.
- Better Image Quality in Bright Conditions: Rear projection screens are less affected by ambient light, making them ideal for well-lit environments.
- Clean Aesthetics: Rear projection setups often look more polished, as the equipment is hidden from view.
Advantages of Rear Projection:
- No Obstructions: Audience members can move freely in front of the screen without casting shadows or blocking the image.
- Enhanced Image Quality: Rear projection screens are typically less affected by ambient light, providing a clearer, brighter image in various lighting conditions.
- Professional Appearance: Rear projection setups offer a clean, professional look, with all equipment hidden behind the screen.
Disadvantages of Rear Projection:
- Higher Cost: Rear projection systems are generally more expensive due to the specialized screens and projectors required.
- Space Requirements: Requires a significant amount of space behind the screen to accommodate the projector and other equipment.
- Complex Installation: Installation can be more challenging and may require professional assistance.
Check out more on Types of Projector Screen.
Front Projection Vs Rear Projection:
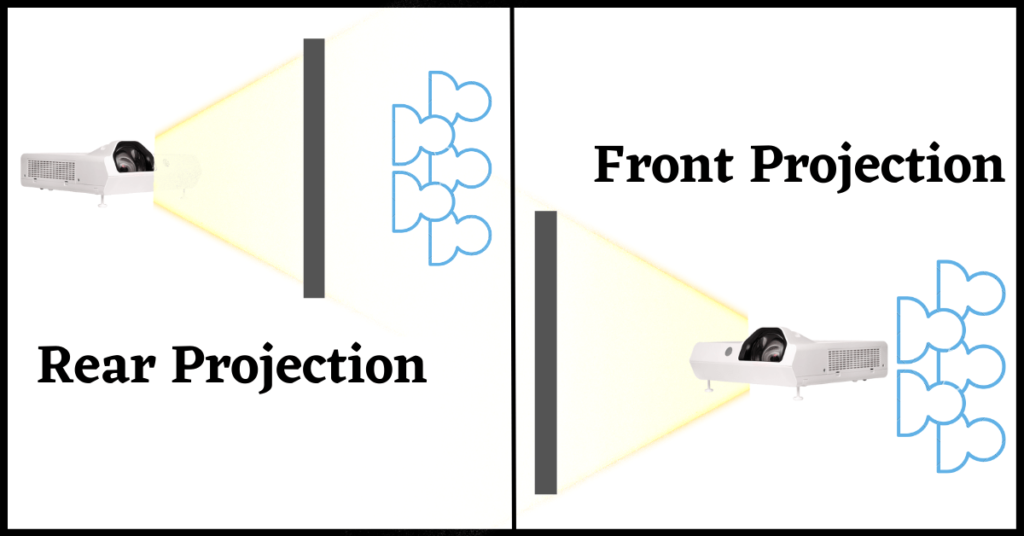
Understanding the difference between front and rear projection is essential for making an informed decision.
When deciding between front and rear projection, it’s crucial to consider various factors such as projection surface, room space, and other specific needs. Let’s explore these aspects to help you make an informed decision.
Choosing between front and rear projection involves understanding their respective advantages and limitations in various aspects. Here’s an in-depth look at each key factor to help you make an informed decision.
1. Setup Location
Front Projection:
- Positioning: In front projection, the projector is placed in front of the screen, facing the audience. This setup requires careful placement to ensure that the projected image is clear and unobstructed.
- Audience Experience: The audience sits behind the projector, which means they may be aware of or interact with the projector and its setup. This positioning can be problematic in high-traffic areas where people might bump into the projector or cables.
Rear Projection:
- Positioning: Rear projection involves placing the projector behind the screen. The image is projected through the screen, which is visible to the audience from the opposite side.
- Audience Experience: This setup allows for a cleaner appearance and reduces the risk of people interacting with the projector. The audience views the image without any obstruction from the equipment, creating a more immersive experience.
2. Space Requirements
Front Projection:
- Space Efficiency: Front projection generally requires less space. The projector is positioned in front of the screen, making it suitable for smaller rooms where space is limited.
- Setup Flexibility: It can be easier to fit a front projector into various room configurations, as long as there is enough space to accommodate the projector’s throw distance.
Rear Projection:
- Space Needs: Rear projection requires significant space behind the screen to accommodate the projector and its setup. This space must be sufficient to house the projector and allow for proper ventilation.
- Setup Constraints: Due to the need for ample space behind the screen, rear projection is better suited for larger rooms or dedicated spaces where space constraints are not an issue.
3. Image Quality
Front Projection:
- Impact of Ambient Light: Front projection can suffer from reduced image quality in bright environments. Ambient light can wash out the projected image, making it less vibrant and clear.
- Optimal Conditions: For best results, front projectors should be used in darker rooms or environments where light can be controlled to avoid affecting image quality.
Rear Projection:
- Brightness and Clarity: Rear projection generally offers better image quality in bright conditions. Since the projector is positioned behind the screen, it is less affected by ambient light, resulting in a more vivid and clearer image.
- Consistent Performance: This setup ensures that the image remains sharp and bright even in environments with some level of ambient light.
4. Aesthetics
Front Projection:
- Visibility of Equipment: The projector and its cables are visible in front projection setups, which can detract from the overall aesthetic of the space. Cables may need to be managed or concealed to improve appearance.
- Impact on Decor: The presence of the projector and associated equipment can be a visual distraction, particularly in settings where a clean, unobtrusive look is desired.
Also, check out How Far to Sit from Projector Screen.
Rear Projection:
- Clean Appearance: Rear projection offers a cleaner, more professional look. The projector is hidden behind the screen, creating a seamless and unobtrusive setup.
- Enhanced Visual Appeal: This setup is often preferred in settings where aesthetics are important, such as in high-end home theaters or corporate environments.

5. Cost
Front Projection:
- Affordability: Front projection is typically more affordable. The initial cost of front projectors and their associated screens is generally lower compared to rear projection setups.
- Maintenance: Maintenance costs are also lower, as the equipment is simpler and requires less specialized support.
Rear Projection:
- Higher Cost: Rear projection setups are generally more expensive. This is due to the need for specialized projectors and screens designed for rear projection.
- Specialized Equipment: The additional costs for rear projector screens, which may include acoustic transparency or other features, contribute to the overall expense.
6. Installation Complexity
Front Projection:
- Ease of Installation: Front projectors are easier to install and set up. Many DIY enthusiasts can handle the installation themselves with minimal technical expertise.
- Setup Flexibility: The installation process is more straightforward, allowing for various mounting options and placement configurations.
Rear Projection:
- Complex Installation: Rear projection setups are more complex and may require professional installation. Proper alignment and calibration are crucial for achieving optimal results.
- Technical Expertise: Professional assistance may be necessary to ensure that the projector and screen are correctly positioned and configured for the best image quality.
7. Projection Surface
Front Projection: Front projectors offer flexibility when it comes to projection surfaces. You can project onto projector screens, walls, or any plain surface. This versatility makes front projectors suitable for various settings, whether at home or in a conference room.
Rear Projection: In contrast, rear projectors require dedicated rear projector screens. However, most modern projector screens are designed to support both front and rear projection. This means you can still use a versatile screen for either setup, though specialized rear projection screens may be needed for optimal results.
Read more about Acoustic/Perforated Screens, which are mostly used for Rear Projection setup.

Elite Screens Aeon CineGrey 3D, CLR/ALR Projector Screen Edge Free Fixed Frame Grey Projector Screen Movie Screen
8. Room Space
Front Projection: Front projectors are generally easier to accommodate in smaller rooms. For a long throw projector, the device should be placed approximately 8-10 feet from the screen. You should also sit about 10 feet from the screen for the best experience. Therefore, a room length of about 10-12 feet is typically sufficient.
Check out How Far Does Projector Need To Be From Screen.
Rear Projection: Rear projection setups require more space. The projector screen must be placed at least 10 feet behind the projector. Consequently, the room size needs to be more than 20 feet to ensure proper placement and seating. This makes rear projection less suitable for smaller rooms and more appropriate for larger venues or events.
Tip: For tighter spaces, consider using an ultra-short throw projector for rear projection, which can be positioned just 1 foot away from the screen. Compare this with standard and long throw projectors to determine what best suits your space.
For detailed comparisons, check out our guide on Ultra Short Throw Vs Short Throw Vs Long Throw Projectors.

Rear Projection vs Front Projection Screens
Modern Screens: Today’s projector screens are often designed to accommodate both front and rear projection. However, for specific rear projection needs, such as in professional settings or theaters, you may require special screens like Acoustically Transparent Projector Screens. These screens allow sound to pass through, which is crucial for maintaining audio quality without external speakers.
Sound Considerations: In front projection, speakers are typically placed in front of the screen. For rear projection, speakers are often positioned behind the screen. Rear projection setups use acoustic or perforated screens that let sound through, mimicking theater setups where speakers are hidden from view but still deliver high-quality audio.
1. Ambient Light
Front Projection: The image quality from a front projector can suffer in bright environments or when ambient light is present. The projection may appear dull if the room is not darkened sufficiently.
Rear Projection: Rear projectors have the advantage of controlling ambient light by darkening the area between the projector and the screen. This setup helps maintain better brightness and image quality even with some level of ambient light.
2. Obstacles
Front Projection: One significant drawback of front projectors is their susceptibility to obstruction. People may bump into the projector or stumble over cables, making them less ideal for high-traffic areas or public events.
Rear Projection: Rear projectors eliminate this issue as the projector sits behind the screen. This setup is less likely to be disturbed by people, making it suitable for public presentations and installations where the area in front of the screen remains clear.
3. Film Making
Historical Use: Rear projection technology was once popular in filmmaking before the advent of green screens. Classic movies used rear projection to create realistic backgrounds while actors performed in front of a screen. This technique avoided shadows that would be cast by front projectors and was more cost-effective compared to large televisions.
For further exploration, watch this video on Rear Projection in Filmmaking.
Front vs Rear Projection: Which Should You Choose?
The choice between front projection vs rear projection depends on your specific needs, environment, and budget. Here’s a quick guide to help you decide:
- Home Theaters: Front projection is often the best choice due to its cost-effectiveness and the ability to control lighting conditions. It’s easier to set up and provides a great cinematic experience in a darkened room.
- Office Presentations: Both front and rear projection can be suitable. However, if you have the space and want to avoid any interruptions or shadows during presentations, rear projection may be the better option.
- Outdoor Events: Rear projection tends to perform better outdoors, as it handles ambient light more effectively and avoids shadows on the screen. If you’re hosting a large outdoor event or showing a movie under the stars, rear projection is likely the better choice.
- Trade Shows and Professional Setups: Rear projection is often preferred in professional environments where image quality, aesthetics, and the avoidance of shadows are critical. It provides a clean, professional look that’s ideal for high-profile events.
FAQs About Front and Rear Projection:
1. Is front or rear projection better?
The answer depends on your specific needs. Front projection is more affordable and easier to set up, making it ideal for home theaters and smaller venues. Rear projection offers better image quality in bright environments and a cleaner setup, but it requires more space and is generally more expensive.
2. Rear projection vs front projection for outdoor use?
Rear projection is often better for outdoor use. It handles ambient light better, ensuring a clearer image, and prevents audience members from casting shadows on the screen.
3. What is the difference between front and rear projection?
The primary difference is the placement of the projector. In front projection, the projector is in front of the screen, while in rear projection, it’s behind the screen. This affects space requirements, image quality, and overall aesthetics.
4. Is rear projection more expensive than front projection?
Yes, rear projection is typically more expensive due to the need for specialized screens and projectors, as well as the complexity of the setup.
5. Can I use a regular projector for rear projection?
Not all projectors are suitable for rear projection. You’ll need a projector that supports rear projection mode and a screen designed for this purpose.
6. What are the space requirements for rear projection?
Rear projection requires significant space behind the screen to accommodate the projector and ensure optimal image quality. The exact amount of space needed depends on the projector’s throw distance.
7. What is the Difference Between Front and Rear Projection Screens?
Front projection screens can be any flat surface, as they don’t require special features. In contrast, rear projection often necessitates the use of acoustic screens, which allow both light and sound to pass through.
Conclusion
Both front and rear projection offer unique benefits, and the right choice for you will depend on your specific circumstances. Whether you’re setting up a home theater, an office presentation space, or an outdoor event, understanding the difference between front projection vs rear projection will help you make an informed decision.
Choose the method that best fits your space, budget, and viewing needs, and enjoy the best possible viewing experience.